Traditional business models often decentralize data management, with each business function storing its own operational data in a separate database. This makes it difficult for employees from different business functions to access each other’s information. Furthermore, duplication of data across multiple departments increases IT storage costs and the risk of data errors. By centralizing data management, SAP software provides multiple business functions with a single view of the truth. This helps companies better manage complex business processes by giving employees of different departments easy access to real-time insights across the enterprise. As a result, businesses can accelerate workflows, improve operational efficiency, raise productivity, enhance customer experiences – and ultimately increase profits.
ERP stands for “enterprise resource planning.” ERP software includes programs for all core business areas, such as procurement, production, materials management, sales, marketing, finance, and human resources (HR). SAP was one of the first companies to develop standard software for business solutions and continues to offer industry-leading ERP solutions.
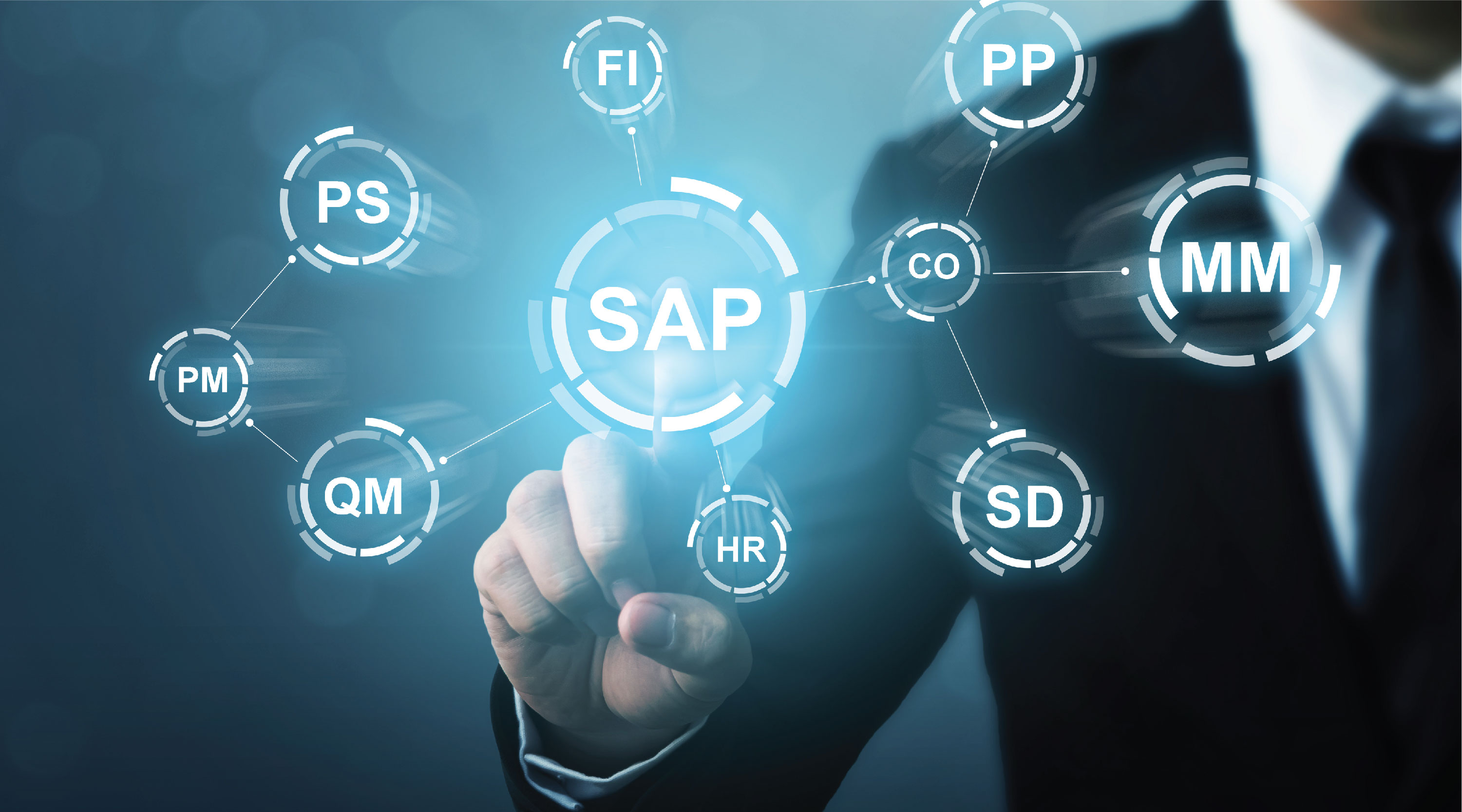


- Cloud ERP
- Business Network
- Business Technology Platform
- CRM and Customer Experience
- Artificial Intelligence
- Spend Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Human Capital Management
- Financial Management
- Small, Medium and Large Enterprises
- Industry Solutions
Application Management Services (AMS) provide support for a customer’s SAP landscape after implementation, following the Service Level Agreement (SLA) and often continuing through the Hypercare Phase. AMS uses tools like the Change Management Process, which guides the authorization, planning, and implementation of changes in production.
Customer-initiated changes that aren't due to malfunctions or predefined as standard are handled through Change Requests, which formally document desired business changes. Pre-approved, low-impact updates are managed as Standard Changes through Request Fulfillment.
Change management covers the entire process from request to implementation, with changes classified by production impact (regular or emergency) and requiring varying levels of approval.
AMS also processes requirements—requests or tasks categorized as incidents, change requests, or service requests. These requests are submitted through a ticketing system or the Service Desk, a central entry point for efficient handling.
Workflow of Service Desk

Receiving requests

Creating message


Monitoring messages


Assigning messages



Reporting
To comply with management reporting and legal requirements, organizations need to produce internal and external reports that document their business transactions. These transactions represent operational and financial movements between other organizations, businesses, or individuals.

The SAP S/4HANA reporting functionality provides a consistent and intuitive UX with the use of HTMLS-based SAPUI5 technology. With the SAP Fiori user interface, reports from different applications are designed to be based on users’ roles, as opposed to SAP ERP’s function-based design. Depending on the role, an SAP Fiori app-based report exposes only relevant data and functions. This user-centric design approach ensures that all elements and fields are useful and easy to consume.
With the embedded approach for reporting in SAP S/4HANA across different applications, business users get synchronized insights quickly within the solution, helping them make better decisions regarding all the information at hand. It enables them to make informed decisions based on real-time insights.
The demand for IT support is reduced with SAP S/4HANA, since business users can create new reports with minimum design-time activities for various self-service reporting and ad-hoc reporting use cases. SAP Fiori-based tools like the Custom Analytical Queries app allow business users to create KPI-based and multidimensional reports for instant insights that require minimal interaction with IT.
SAP software customization refers to modifying and configuring the standard functionalities of SAP applications to meet the unique requirements of a business. It involves adapting the software to align with the organization’s workflows, business processes, and industry-specific needs. Customization allows businesses to leverage the full potential of SAP software and optimize its capabilities according to their specific goals.
Every organization has its own unique set of business requirements. Customization allows businesses to align their SAP software with these requirements, ensuring that the system supports their specific processes and workflows. This alignment enhances operational efficiency, reduces manual workarounds, and improves overall productivity.
SAP software customization enables businesses to optimize their processes by tailoring the system to their specific needs. By streamlining workflows and eliminating unnecessary steps, organizations can improve efficiency, reduce errors, and enhance the accuracy of data captured within the system. This optimization leads to time and cost savings, as well as improved decision-making capabilities.
Customization allows businesses to create user-friendly interfaces and configurations that resonate with their employees. By incorporating intuitive design elements and personalized features, organizations can enhance user adoption and satisfaction. This, in turn, leads to increased productivity and reduced training efforts.